The Lunacoin Trend: The Ultimate Guide to Cryptocurrency and the Future of the Dollar
There's no doubt that cryptocurrency is on the rise. Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin and other currencies have seen meteoric rises in value over the past year or so. But what is driving this trend? And where is it going? In this article, we will look at Lunacoin – one of the most popular cryptocurrencies – and explore its future implications for the global economy.

According to Jan Lansky, a cryptocurrency is a system that meets six conditions:
- The system does not require a central authority; its state is maintained through distributed consensus.
- The system keeps an overview of cryptocurrency units and their ownership.
- The system defines whether new cryptocurrency units can be created. If new cryptocurrency units can be created, the system defines the circumstances of their origin and how to determine the ownership of these new units.
- Ownership of cryptocurrency units can be proved exclusively cryptographically.
- The system allows transactions to be performed in which ownership of the cryptographic units is changed. A transaction statement can only be issued by an entity proving the current ownership of these units.
- If two different instructions for changing the ownership of the same cryptographic units are simultaneously entered, the system performs at most one of them.
In March 2018, the word cryptocurrency was added to the Merriam-Webster Dictionary
Lunacoin is a digital or virtual currency that uses cryptography to secure its transactions and control the creation of new units. Cryptocurrency is decentralized, meaning it is not subject to government or financial institution control. The underlying technology behind Lunacoin is blockchain, which is a distributed ledger system that records all transactions chronologically and publicly. This transparency makes it virtually impossible to counterfeit or double-spend Lunacoin.
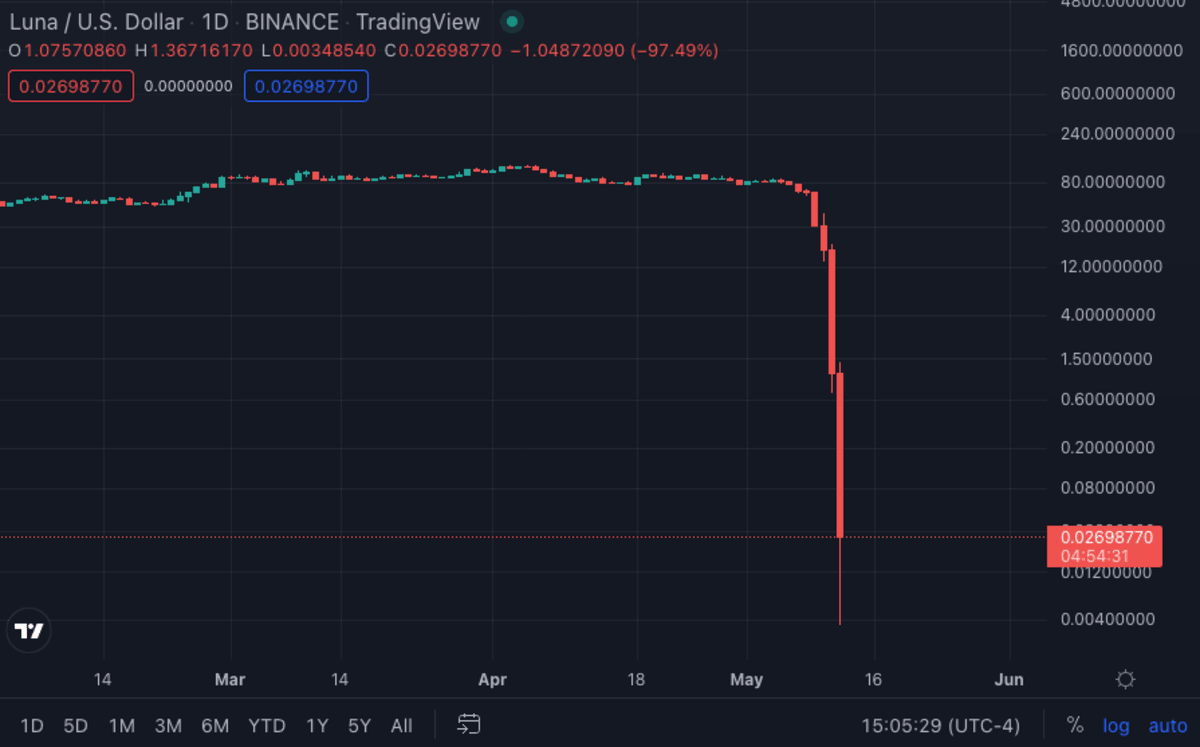
What influenced the crash of lunacoin?
The Lunacoin trend can be traced back to early 2017, when the price of Bitcoin started to climb rapidly. This was followed by a surge in interest in other cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum, Litecoin and Monero. The total market value of all cryptocurrencies reached an all-time high of over $800 billion in January 2018. However, the prices of all cryptocurrencies then crashed in early 2018, with the total market value falling to around $300 billion by mid-2018. The main factors that caused the crash were:
- Regulatory concerns: In late 2017, China banned Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs) and closed down cryptocurrency exchanges. This was followed by similar actions from other countries, such as South Korea and the United States.
- Concerns about the future of cryptocurrency: There was a lot of speculation about whether cryptocurrencies would survive in the long-term. This caused many people to sell their cryptocurrencies, leading to the price crash.
- Technical issues: The Bitcoin network experienced two hard forks in 2017, which led to the creation of new cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin Cash and Ethereum Classic. This caused confusion among investors and led to selling.
What is the future of lunacoin?
Despite the crash in 2018, Lunacoin has continued to grow in popularity and its price has steadily risen since mid-2018. The main reasons for this are:
- Increasing mainstream adoption: Cryptocurrencies are being increasingly accepted by businesses and individuals. For example, Microsoft, AT&T and Overstock all accept Bitcoin as payment.
- Improved regulation: Governments are starting to create regulations around cryptocurrencies, which is giving investors more confidence in the future of these assets.
- Development of new technologies: The launch of new platforms, such as the Lightning Network, is making it easier to use and store cryptocurrencies.
Who mainly dabbles in cryptocurrency?
Elon Musk, CEO of Tesla and SpaceX, is a fan of cryptocurrency. He has invested in Bitcoin and Ethereum. In February 2018, he even tweeted that he was “ considering taking Tesla private at $420”
MicroStrategy, a Nasdaq-listed business intelligence company, has also been buying up Bitcoin. As of August 2020, the company holds more than 70,000 BTC.
Doomsday preppers are also increasingly turning to cryptocurrency as a hedge against economic collapse. If the dollar were to tank, their Bitcoin holdings would theoretically increase in value. Preppers are also buying up pallets of bulk survival food buckets because they see the strength of the dollar is faltering.
The rise of cryptocurrency is often compared to the dotcom bubble of the late 1990s. Just as there were many fraudulent companies during the dotcom boom, there are also many scams in the cryptocurrency space. Investors should be careful when buying into any digital currency and always do their research beforehand.
What is the future of the dollar?
The future of the dollar is uncertain. With increasing national debt and quantitative easing, many are concerned that the dollar will eventually lose its status as the world's reserve currency. If this were to happen, it would have serious implications for the global economy. For now, cryptocurrency remains a niche market, but its popularity is on the rise. Only time will tell what the future holds for Lunacoin and other digital currencies.
Lunacoin's popularity is due to a number of factors. Firstly, it has a limited supply of only 21 million coins, which creates scarcity and drives up demand. Secondly, it is fast and cheap to send money anywhere in the world using Lunacoin. And finally, Lunacoin is highly volatile, which makes it an attractive investment for speculative traders.
So what does the future hold for Lunacoin?
Many experts believe that the price of Lunacoin will continue to rise as more people become aware of its existence and advantages over traditional fiat currencies. Some even predict that Lunacoin could eventually replace the dollar as the reserve currency of the world. While this may seem far-fetched, it is not impossible. Remember, just a few years ago nobody had heard of Bitcoin – and now it is a household name.
Is crypto affected by inflation?
The short answer is no. Cryptocurrency is not subject to the effects of inflation. The reason for this is that cryptocurrency is not controlled by any government or financial institution. Instead, it is decentralized, meaning it is not subject to government or financial institution control.
How do you convert crypto to US Dollar?
There are a few different ways to convert cryptocurrency to US Dollar. The most popular way is to use a cryptocurrency exchange. Cryptocurrency exchanges are online platforms where you can buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies. Another way to convert cryptocurrency to US Dollar is to use a peer-to-peer platform. Peer-to-peer platforms are online marketplaces that allow you to buy, sell, or trade cryptocurrencies without the need for a third-party exchange. Finally, you can also convert cryptocurrency to US Dollar by using a cryptocurrency ATM. Cryptocurrency ATMs are machines that allow you to insert cash and receive cryptocurrency in return.
What Is a cashless society?
A cashless society is one where people no longer use paper money or coins, and instead rely on electronic payments for all transactions. This could be via credit cards, debit cards, mobile apps or other digital methods.
There are a number of reasons why a cashless society might be beneficial. For example, it would reduce crime as there would be no paper money to steal. It would also make it easier for businesses to track their sales and customers.
However, there are also some drawbacks to a cashless society. For example, it would be easier for the government to track people's spending and could lead to more surveillance. Additionally, if the power went out or the internet went down, people would be unable to make or receive payments.
So far, Sweden is leading the way in terms of moving towards a cashless society. In 2015, only six percent of Swedes used cash for their purchases. This figure is likely to continue to fall as more and more businesses stop accepting cash.
What does this mean for the future of the dollar?
If more and more countries move towards a cashless society, it could have serious implications for the future of the dollar. As the world's reserve currency, the majority of global trade is conducted in dollars. If other countries start to use different currencies, or if digital currencies become more popular, the demand for dollars could decrease. This could lead to inflation and a devaluation of the dollar.
Understanding a Blockchain: Crypto's digital ledger
A blockchain is a digital ledger that records all transactions that take place in a given system. It is decentralized, meaning that it is not controlled by any one person or institution. Instead, it is maintained by a network of computers that are constantly verifying and updating the data.
Blockchains are secure and transparent, and have many potential applications in a variety of industries. For example, they could be used to create a more efficient and secure supply chain management system.
What is the history of blockchains?
The concept of the blockchain was first introduced in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin. In Nakamoto's original paper, he described how a decentralized ledger could be used to record and verify all transactions made within a given system.
Since then, the idea of the blockchain has been further developed and applied to a variety of different industries. In 2015, a group of companies and organizations came together to form the Hyperledger Project, with the goal of developing blockchain technology for use in business.
What are some potential applications of blockchains?
As mentioned above, blockchains have the potential to be used in a variety of different industries. Some potential applications include:
- Supply chain management
- Identity management
- Voting
- Property ownership records
- Copyright protection
Blockchains are secure and transparent, and have many potential applications in a variety of industries. With their ability to streamline processes and reduce costs, it's likely that we will see more and more businesses adopting this technology in the future.
What is the difference between a blockchain and a database?
A database is a centralized, digital storage system that allows people to store, update, and retrieve data. A blockchain is a decentralized, digital ledger that records all transactions that take place in a given system. Blockchains are more secure and efficient than databases, and have many potential applications in a variety of industries.
Lunacoin in the news
In May 2019, a story about a man who bought $25 worth of Lunacoin in 2009 and forgot about it went viral. The man, known only as “PizzaGuy”, woke up to find that his investment was now worth over $100 million.
This story helped to increase the visibility of Lunacoin and attracted a lot of new investors.
In June 2019, Lunacoin was listed on the Coinbase Pro exchange, which gave it a major boost in credibility.
Lunacoin is still relatively unknown compared to other cryptocurrencies, but its popularity is growing steadily. With a limited supply and increasing demand, the price of Lunacoin is likely to continue to rise in the future.
List of Crypto Currencies
0–9
A
B
- List of bitcoin forks
- Bitcoin Magazine
- Bitcoin scalability problem
- Bitfinex
- Bithumb
- BitLicense
- Blockchain
- Blockchain game
- Cryptocurrency bubble
C
- Christian Catalini
- Chainlink (blockchain)
- Chamber of Digital Commerce
- Circle (company)
- Cloud mining
- The Cobden Centre
- Coincheck
- CoinDesk
- Colored Coins
- Complementary currency
- Counterparty (platform)
- Crypto naming controversy
- Crypto.com
- Cryptocurrencies in Europe
- Cryptocurrencies in Puerto Rico
- Cryptocurrency and crime
- Cryptojacking
- CryptoNote
D
- The DAO (organization)
- Decentraland
- Decentralized application
- Decentralized finance
- Dfinity
- Double-spending
- Dusting attack
E
F
G
H
I
L
M
N
P
- PayPal
- Perpetual futures
- Polkadot (cryptocurrency)
- Proof of identity (blockchain consensus)
- Proof of personhood
- Proof of space
- Proof of Space and Time
- Proof of stake
- Proof of work
R
S
- Safuu
- Security token offering
- Smart contract
- Social token
- SpankChain
- Stablecoin
- Stacks blockchain
- Steemit
T
U
V
W
Z
Whether Lunacoin will fulfill its potential remains to be seen. But one thing is for sure: cryptocurrency is here to stay, and it is reshaping the way we think about money. So whatever your opinion on Lunacoin, make sure you do your own research and stay up to date with this rapidly evolving industry. Who knows, you may be the one cashing in on the next big thing.
What are your thoughts on Lunacoin? Do you think it has the potential to replace the dollar? Let us know in the comments below!
Please note that this is not investment advice and we do not recommend investing in any cryptocurrency. Cryptocurrencies are highly volatile and risky investments. Do your own research before making any investment decisions. always consult a financial advisor.
List of cryptocurrencies and when they were introduced:| Year of introduction | Currency | Symbol | Founder(s) | Hash algorithm | Programming language of implementation | Consensus mechanism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2009 | Bitcoin | BTC,[2] XBT, ₿ | Satoshi Nakamoto[nt 1] | SHA-256d[3][4] | C++[5] | PoW[4][6] | The first and most widely used decentralized ledger currency,[7] with the highest market capitalization.[8] |
| 2011 | Litecoin | LTC, Ł | Charlie Lee | Scrypt | C++[9] | PoW | One of the first cryptocurrencies to use scrypt as a hashing algorithm. |
| 2011 | Namecoin | NMC | Vincent Durham[10][11] | SHA-256d | C++[12] | PoW | Also acts as an alternative, decentralized DNS. |
| 2012 | Peercoin | PPC | Sunny King (pseudonym)[citation needed] |
SHA-256d[citation needed] | C++[13] | PoW & PoS | The first cryptocurrency to use both PoW and PoS functions. |
| 2013 | Dogecoin | DOGE, XDG, Ð | Jackson Palmer & Billy Markus[14] |
Scrypt[15] | C++[13] | PoW | Based on the Doge internet meme. |
| 2013 | Gridcoin | GRC | Rob Hälford[16] | Scrypt | C++[17] | Decentralized PoS | Linked to citizen science through the Berkeley Open Infrastructure for Network Computing[18] |
| 2013 | Primecoin | XPM | Sunny King (pseudonym)[citation needed] |
1CC/2CC/TWN[19] | TypeScript, C++[20] | PoW[19] | Uses the finding of prime chains composed of Cunningham chains and bi-twin chains for proof-of-work. |
| 2013 | Ripple[21][22] | XRP | Chris Larsen & Jed McCaleb[23] |
ECDSA[24] | C++[25] | "Consensus" | Designed for peer to peer debt transfer. Not based on bitcoin. |
| 2013 | Nxt | NXT | BCNext (pseudonym) |
SHA-256d[26] | Java[27] | PoS | Specifically designed as a flexible platform to build applications and financial services around its protocol. |
| 2014 | Auroracoin | AUR | Baldur Odinsson (pseudonym)[28] |
Scrypt | C++[29] | PoW | Created as an alternative currency for Iceland, intended to replace the Icelandic króna. |
| 2014 | Dash | DASH | Evan Duffield & Kyle Hagan[citation needed] |
X11 | C++[30] | PoW & Proof of Service[nt 2] | A bitcoin-based currency featuring instant transactions, decentralized governance and budgeting, and private transactions. |
| 2014 | NEO | NEO | Da Hongfei & Erik Zhang | SHA-256 & RIPEMD160 | C#[31] | dBFT | China based cryptocurrency, formerly ANT Shares and ANT Coins. The names were changed in 2017 to NEO and GAS. |
| 2014 | MazaCoin | MZC | BTC Oyate Initiative | SHA-256d | C++[32] | PoW | The underlying software is derived from that of another cryptocurrency, ZetaCoin. |
| 2014 | Monero | XMR | Monero Core Team | RandomX | C++[33] | PoW | Privacy-centric coin based on the CryptoNote protocol with improvements for scalability and decentralization. |
| 2014 | Titcoin | TIT | Edward Mansfield & Richard Allen[34] | SHA-256d | TypeScript, C++[35] | PoW | The first cryptocurrency to be nominated for a major adult industry award.[36] |
| 2014 | Verge | XVG | Sunerok | Scrypt, x17, groestl, blake2s, and lyra2rev2 | C, C++[37] | PoW | Features anonymous transactions using Tor. |
| 2014 | Stellar | XLM | Jed McCaleb | Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP) [38] | C, C++[39] | Stellar Consensus Protocol (SCP) [38] | Open-source, decentralized global financial network. |
| 2014 | Vertcoin | VTC | David Muller[40] | Verthash[41] | C++[42] | PoW | Aims to be ASIC resistant. |
| 2015 | Ethereum | ETH, Ξ | Vitalik Buterin[43] | Ethash[44] | C++, Go[45] | PoW, PoS | Supports Turing-complete smart contracts. |
| 2015 | Ethereum Classic | ETC | EtcHash/Thanos[46] | PoW | An alternative version of Ethereum[47] whose blockchain does not include the DAO hard fork.[48] Supports Turing-complete smart contracts. | ||
| 2015 | Nano | Nano | Colin LeMahieu | Blake2 | C++[citation needed] | Open Representative Voting[49] | Decentralized, feeless, open-source, peer-to-peer cryptocurrency. First to use a Block Lattice structure. |
| 2015 | Tether | USDT | Jan Ludovicus van der Velde[50] | Omnicore[51] | PoW | Tether claims to be backed by USD at a 1 to 1 ratio. The company has been unable to produce promised audits.[52] | |
| 2016 | Firo | FIRO | Poramin Insom[53] | Merkle tree Proof[54] | C++[55] | PoW | The first financial system employing Zero-knowledge proof to protect users' privacy.[53] It conducted the world's first large-scale blockchain election for Thailand Democrat Party in 2018.[56] |
| 2016 | Zcash | ZEC | Zooko Wilcox | Equihash | C++[57] | PoW | The first open, permissionless financial system employing zero-knowledge security. |
| 2017 | Bitcoin Cash | BCH[58] | SHA-256d | PoW | Hard fork from bitcoin, increased maximum block size from 1MB to 8MB (as of 2018, 32MB) | ||
| 2017 | EOS.IO | EOS | Dan Larimer | WebAssembly, Rust, C, C++[59] | delegated PoS | Feeless Smart contract platform for decentralized applications and decentralized autonomous corporations with a block time of 500 ms.[59] | |
| 2017 | Cardano | ADA, ₳ | Charles Hoskinson | Ouroboros, PoS Algorithm[60] | Haskell[61] | PoS | A proof-of-stake blockchain platform: developed through evidence-based methods and peer-reviewed research.[62][63][64] |
| 2017 | TRON | TRX | Justin Sun | Java, Solidity[65] | |||
| 2018 | AmbaCoin | official cryptocurrency of the Cameroonian separatist entity of Ambazonia | |||||
| 2019 | Algorand | ALGO | Silvio Micali | Go[66] | PoS | Uses a verifiable random function to randomly select groups of users to certify blocks.[67] | |
| 2020 | Avalanche | AVAX | Emin Gün Sirer, Kevin Sekniqi, Maofan “Ted” Yin | PoS | |||
| 2020 | Shiba Inu | SHIB | Ryoshi | PoS | |||
| 2020 | Polkadot | DOT | Gavin Wood | Rust | PoS | ||
| 2021 | DeSo | DESO | Nader al-Naji (aka diamondhands)[68] | Go[69] | PoW[70] | Also a social media platform, resembling Twitter.[71][72] Known as BitClout until September 2021.[68] | |
| 2021 | SafeMoon | SAFEMOON | SafeMoon LLC | Solidity[73] | PoW | ||
| 2021 | Internet Computer | ICP |
Dominic Williams, DFINITY Foundation |
Rust[74] |
Cryptocurrency Terms, Definitions & Jargon
Decentralized API (dAPI)
Shielded Transaction
0x Protocol
1hr
24hr
30d
51% Attack
7d
Abstract
Account
Accounting Token
Accumulation/Distribution Indicator
Adam Back
Adaptive State Sharding
Address
Adoption Curve
Aeternity Blockchain
Air Gap
Airdrop
Airnode
Algo-Trading (Algorithmic Trading)
Algorithm
Algorithmic Market Operations (AMOs)
Algorithmic Stablecoin
All-Time-High (ATH)
All-Time-Low (ATL)
Allocation
Alpha Version
Alphanumeric
Altcoin
Altcoin Trader
Amazon S3
AMLD5
Anarcho-capitalism
Angel Investor
Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
Annual Percentage Yield (APY)
Anonymous
Anti-dump/Anti-Dumping Policy
Anti-Fragile
Anti-Malware
Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Antivirus
Apeing
API
Application Layer
AR Token (Arweave)
Arbitrage
Aroon Indicator
Ashdraked
ASIC
ASIC-Resistant
Ask Price
Asset-Backed Tokens
Assets Under Management (AUM)
Astroturfing
Asynchronous
Atomic Swap
AtomicDEX
Attestation Ledger
Auction
Audit
Augmented Reality (AR)
Authentication
Automated Market Maker (AMM) [Updated]
Autonomous Economic Agent (AEA)
Average Directional Index (ADX)
Bag
Bagholder
Bakers
Baking
Bandwidth
Bank for International Settlements (BIS)
Banking as a Service (BaaS)
Banking Secrecy Act (BSA)
Basket
Batch Auctions
Beacon Chain
Bear
Bear Market
Bear Trap
Bearwhale
Benchmark
Benchmark Index
BEP-2 (Binance Chain Tokenization Standard)
BEP-20
BEP-721
BEP-95 (Bruno Hard Fork Upgrade)
Beta (Release)
Bid Price
Bid-Ask Spread
Big Tech
Binance Labs
Binance Launchpad
Binary Code
Bit
Bitcoin ATM (BTM)
Bitcoin Dominance (BTCD)
Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (BIP)
Bitcoin Pizza
Bitcoiner
Bitcointalk
BitLicense
BitPay
Bits
Bitstream
Black Hat Hacker
Black Swan Event
Blake-256
Block
Block Explorer
Block Header
Block Height
Block Producer
Block Reward
Block Size
Block Time
Block Trade
Blockchain
Blockchain 1.0
Blockchain 2.0
Blockchain 3.0
Blockchain Explorer
Blockchain Transmission Protocol (BTP)
Blockchain Trilemma
Blockchain-Enabled Smart Locks
Bollinger Band
Bonding Curve
Bots
Bounty
Brave Browser
Breaking
Brian Armstrong
Bridges
Browser Extension
Brute Force Attack (BFA)
Bubble
Bug Bounty
Bug Exploit
Bull
Bull Market
Bull Run
Bull Trap
Burn/Burned
Buy The (F*******) Dip (BTD/BTFD)
Buy Wall
Byron Phase
Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT)
Byzantine Generals’ Problem
Byzantium Fork
C++
Call Options
Candlesticks
Capital
Capital Efficiencies
Capital Funds
Capitulation
Casascius Coin
Cash
Casper (Ethereum)
Cathie Wood
CeDeFi
Censorship
Censorship Resistance
Central Bank
Central Bank Digital Currency
Central Ledger
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Centralized
Centralized Exchange (CEX)
Centre (Consortium)
Certificate of Deposit (CD)
Chain Reorganization
Chain Split
Change
Change Address
Changpeng Zhao (CZ)
Chargeback
Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME)
Chunk (NEAR)
Cipher
Ciphertext
Circle
Circulating Supply
Client
Close
Cloud
Cloud Mining
Co-Signer
Code
Coin
Coin Mixer
Coinbase
Coinbase Transaction
Cold Storage
Cold Wallet
Collateral
Collateral Tokens
Collateralization
Collateralized Debt Obligation
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP)
Collateralized Mortgage Obligation (CMO)
Collateralized Stablecoin
Commingling
Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC)
COMP Token
Composable DeFi
Composable Token
Concentrated Liquidity
Confirmation
Confirmations
Consensus
Consensus Mechanism
ConsenSys
Consortium Blockchain
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Contract
Contract Account
Contract for Difference (CFD)
Coordinator
Core Wallet
Corporate Treasury
Correction
CPU Miner
Craig Wright
Craig Wright
Credit Rating
Credit Risk
Cross Margin
Cross-Border Trading
Cross-Chain
Cross-Chain Communication
Crowdfunding
Crowdloan
Crypto Debit Card
Crypto Invoicing
Cryptoasset
Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency Money Laundering
Cryptocurrency Pairs
Cryptographic Hash Function
Cryptography
Cryptojacking
Cryptology
CryptoPunks
Currency
Currency Crisis
Curve AMO
Custodial
Custodian
Custody
Cypherpunk
Daedalus Wallet
DAO Summoning
Dark Web
Darknodes
Data Privacy
Data Scraping
Date of Launch
Day Trading
Dead Cat Bounce
Dead Coin
Death Cross
Decentralization Maximalism
Decentralization Ratio
Decentralized
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Decentralized Autonomous Initial Coin Offerings (DAICO)
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAO)
Decentralized Currency
Decentralized Database
Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
Decentralized Governance
Decentralized Identifier (DID)
Decentralized Marketplace
Decentralized Network
Decentralized Payment Network
Decentralized Social Media
Decentralized Stablecoin
Decryption
Deep Web
DeFi
DeFi Aggregator
DeFi Degens
Deflation
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (dPOS)
Delisting
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attack
Depth Chart
Derivative
Derivatives Market
Desktop Wallet
Deterministic Wallet
Dex Aggregator
Dharma Protocol
Diamond Hands
Difficulty
Digital
Digital Art
Digital Asset
Digital Asset Custodian
Digital Asset Ecosystem
Digital Barter Economy
Digital Commodity
Digital Currency
Digital Dollar
Digital Identity
Digital Signature
Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA)
Dildo
Dip
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
Discord
Distributed Consensus
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack
Distributed Ledger
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
Distributed Network
Diversification
Documentation
Dolphin
Dominance
Dorian Nakamoto
DotSama
Double Spend Attack
Double Spending
Drawdown
Dual-Token Economy/Model (Two-Token Economy)
Dump
Dumping
Dust Transactions
Dusting Attack
DYCO (Dynamic Coin Offering)
DYOR
E-Signature
Economic Utility
Edge Nodes
Effective Proof-of-Stake
Electrum Wallet
ELI5
Elliott Waves
EMA (Exponential Moving Average)
Email Spoofing
Emission
Encryption
Enterprise Blockchain
Enterprise Ethereum Alliance (EEA)
Epoch
Equity
Erasure Encoding
ERC-1155
ERC-20
ERC-223
ERC-721
ERC-777
ERC-827
ERC-884
ERC-948
Escrow
Esports
Ethash
Ether
Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP)
Ethereum Request For Comment (ERC)
Ethereum Transaction
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
Event Triggers
Exchange
Exchange Traded Fund (ETF)
Exit Scam
Falling Knife
Falling Wedge
Fan Token
FATF Travel Rule
Faucet
Fee Tiers
Fiat
Fiat On-Ramp
Fiat-Pegged Cryptocurrency
Fibonacci Retracement Level
Field Programmable Gate Array
Financial Action Task Force (FATF)
Financial Crime Enforcement Network (FinCEN)
Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre (FINTRAC)
First In, First Out
First-Mover Advantage (FMA)
Fish
Flash Crash
Flash Loan
Flash Loan Attack
Flash Loans
Flippening
Flipping
FOMO
Fork (Blockchain)
Fork (Software)
Fractional Stablecoins
Fraud Proof
Front Running
FUD [2021]
FUDster
Full Node
Fully Diluted Value (FDV)
Fully Homomorphic Encryption
Fundamental Analysis (FA)
Funding Payments
Fungible
Futures
Gains
Game Channels
Game Theory
GameFi
Gas
Gas Limit
Gas Price
Gas Station Networks (GSN)
Gavin Wood
Gems
Genesis Block
Geotagged NFT
Geth
GitHub
Gold-Backed Cryptocurrency
Golden Cross
Google Authenticator
Governance
Governance Token
Graphical Processing Unit (GPU)
Greater Fool Theory
Green Candle
Group Mining
Gwei
Hacking
Hal Finney
Halving
Hard Cap
Hard Fork (Blockchain)
Hard Fork Combinator
Hard Peg
Hardware Security Module
Hardware Wallet
Hash
Hash Function
Hash Power / Hash Rate
Hedge Contract
Hidden Cap
Hierarchical Deterministic Wallet (HD Wallet)
HODL
Honeyminer
Hostage Byte Attack
Hosted Wallet
Hot Storage
Hot Wallet
Howey Test
Huobi BTC (HBTC)
Hybrid PoW/PoS
Hyperinflation
Hyperledger (Hyperledger Foundation)
Immutable
Impermanent Loss
In-the-Money / Out-of-the-Money
Infinite Approval
Infinite Mint Attack
Inflation
Initial Bounty Offering (IBO)
Initial Coin Offering (ICO)
Initial Dex Offering (IDO)
Initial Exchange Offering
Initial Farm Offering (IFO)
Initial Game Offering (IGO)
Initial NFT Offering (INO)
Initial Public Offering (IPO)
Initial Stake Pool Offering (ISPO)
Initial Token Offering (ITO)
Input-Output Hong Kong (IOHK)
Insider Trading
Instamine
Instant Settlement Network Layer
Institutional Investor
Insurance Fund
Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
Intellectual Property (IP)
Intercontinental Exchange (ICE)
Interest Rates
Intermediary/Middleman
Internal Transaction
Internet Layer
Internet Memes
Internet of Things
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
Interoperability
InterPlanetary File System (IPFS)
Intrinsic Value
Invest
Investment Vehicles (Crypto-tied)
IOU
IP Address
Isolated Margin
Lachesis
Lambo
Large Cap
Laser Eyes
Law of Accelerating Returns
Layer 0
Layer 2
Layer-1 Blockchain
Ledger
Leverage
Leveraged Tokens
libp2p
Light Node
Lightning Network
Limit Order
Limit Order/Limit Buy/Limit Sell
LINK (Chainlink)
Liquid Market
Liquid Staking (Fantom)
Liquidation
Liquidity
Liquidity Bootstrapping Pool (LBP)
Liquidity Mining
Liquidity Pool
Liquidity Provider
Liquidity Provider Tokens (LP Tokens)
Liveness
Location Swap
Long
Longing (Long Position)
Lovelace
Mainnet
Mainnet Swap
Maker Protocol (MakerDAO)
Malware
Man-in-the-Middle Attack (MITM)
Margin Call
Margin Trading
Market
Market Balances
Market Capitalization/Market Cap/MCAP
Market Maker, Market Taker
Market Order/Market Buy/Market Sell
Market Signal
Marlowe
Masternodes
Max Supply
Medium of Exchange
Megahashes Per Second
Meme Economy
Memecoin
Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
Mempool
Mercenary Capital
Merkle Tree
MetaMask
Metatransaction
Metaverse
Metaverse-as-a-Service (MaaS)
Metcalfe’s Law
Micro Cap
MicroBitcoin (uBTC)
Micropayment
Microtransaction
Mid Cap
MilliBitcoin
Mimetic Theory
Mineable
Minecraft
Miner Extractable Value (MEV)
Miners
Minimum Collateralization Ratio (MCR)
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Mining
Mining Algorithm
Mining as a Service (MaaS)
Mining Contract
Mining Difficulty
Mining Farm
Mining Pool
Mining Reward
Mining Rewards
Mining Rig
Minnow
Minting
Mnemonic Phrase
Mnemonics
Mobile Wallet
Moloch DAO
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
Monetary Policy
Money
Money Flow Index (MFI)
Money Laundering
Money Market
Money Transfer License
Money Transmitter
Moon
Moore's Law
Motoko Programming Language (DFINITY)
Moving Average (MA)
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD)
Mt. Gox
Multi-Coin Wallet
Multi-level Marketing
Multi-Party Computation
Multi-Party Computation as-a-Service
Multi-Signature (Multi-Sig)
Multisignature
My Story (VeChain)
Odysee
Off-Chain
Off-Chain Governance
Off-Chain Transaction
Off-Ledger Currency
Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC)
Offline Storage
Offshore Account
OHM Fork
On-Balance Volume (OBV)
On-Chain
On-Chain Governance
On-Ledger Currency
One Cancels the Other Order (OCO)
Online Storage
Ontorand Consensus Engine (Ontology)
Open Source
Open/Close
OpenSea [2021]
Opera Mainnet (Fantom)
Operating System (OS)
Optimistic Oracle
Optimistic Rollup
Option
Options Market
Oracle Manipulation
Oracles
Order Book
Orphan
Orphaned Block
Ouroboros Praos
Over-Collateralization
Over-the-Counter (OTC)
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Trading
Overbought
Oversold
Pair
Paper Trading
Paper Wallet
Parachain
Participation Node
Passive Income
Password Manager
Paul Le Roux
Payee
Peer-to-Peer (P2P)
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending
Peg
Pegged Currency
Permissioned Ledger
Permissionless
Perpetual Contracts
Phishing
Phone Phishing
Physical Bitcoins
Platform
Play-to-Earn (Play2Earn)
Play2Earn (Play-to-Earn)
Player Payout
Plutus (Cardano)
Politeia (Decred)
Ponzi Scheme
Portfolio
Position Size
Post-Mine
Pre-IDO
Pre-Mine
Pre-Sale
Prediction Market
Price Impact
Private Blockchain
Private Key/Secret Key
Procedural Programming
Profit and Loss (P&L) Statement
Programmability
Proof of Attendance Protocol
Proof-of-Authority (PoA)
Proof-of-Burn
Proof-of-Burn (PoB)
Proof-of-Developer (PoD)
Proof-of-Donation
Proof-of-History (PoH)
Proof-of-Immutability (PoIM)
Proof-of-Replication
Proof-of-Spacetime
Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
Proof-of-Validation
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Protocol
Protocol Layer
Pseudonymous
Public Address
Public Blockchain
Public Key
Public Sale
Public-Key Cryptography
Public-Key Infrastructure
Pump and Dump (P&D) Scheme
Pure Proof of Stake (PPoS)
Put Option
Pyramid Scheme
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID)
Rage-quit
Raiden Network
Rank
Ransomware
Rebalancing
Rebase
Recovery Seed
Redundancy
Regional/Local/Community Currencies
Regulated
Regulatory Compliance
Rehypothecation
Rehypothecation
REKT
Relative Strength Index (RSI)
Relay Chain
Relay Nodes
Renewable Energy
Repair Miners
Replay Attack
Replicated Ledger
Resistance (Line/Level)
Retargeting
Revenue Participation Tokens
Reverse Indicator
Ring CT (Confidential Transactions)
Ring Miners
Ring Signature
Roadmap
Roger Ver
ROI
Roth IRA
Rug Pull
Rust
Ryuk Ransomware
S&P 500 (Standard and Poor's 500)
Satoshi (SATS)
Satoshi Nakamoto
Scaling Problem
Scaling Solution
Scam
Scamcoin
Scammer
Scholarship/Scholar
Script
Scrypt
Second-Layer Solutions
Secondary Market
Secure Element
Secure Multi-Party Computation (sMPC)
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
Security
Security Token
Security Token Offering
Seed Phrase
Segregated Witness (SegWit)
Selfish Mining
Sell Wall
Semantic Web
Settlement
Settlement Layer
SHA-256
Shard
Shard Chain
Sharding
Shelley Phase
Shielded Address
Shilling
Shitcoin
SHO (Strong Holder Offering)
Short
Side Chain
Side Channel Attack
Signal
Silk Road
SIM-Swap
Simplified Payment Verification (SPV)
Skynet
Slippage
Slot (Cardano)
Smart Contract
Smart Contract Audit
Smart Home
Smart Token
Snapshot
Social Engineering
Soft Cap
Soft Fork (Blockchain)
Soft Peg
Software Library
Software Stack
Software Wallet
Solidity
Source Code
SPAC
Spear Phishing
Speculative Investment
Spoon (Blockchain)
Spot
Spot Market
Spot Trading
Spyware
Stablecoin
Staking
Staking Pool
Stale Block
State Channel
Stochastic Oscillator
Stop-Loss Order
Storage (Decentralized)
Storage Miners
Store of Value
Subgraph Manifest
Substrate
Supercomputer
Supply and Demand
Supply Chain
Supply Chain Attack
Swarm
Swing Failure Pattern (SFP)
Swing Trading
Sybil Attack
Symbol
Synthetic Asset
Taint
Tamper-Proof Ledger
Tangle
Taproot
Technical Analysis/Trend Analysis (TA)
Technical Indicators
Terahashes Per Second
Testnet
The Cantillon Effect
The DAO
Think Long Term (TLT)
This Is Gentlemen
Throughput
Ticker
Ticker Symbol
Time-Weighted Automated Market Maker (TWAMM)
Time-weighted Average Price (TWAP)
Timelock/Locktime
Timestamp
Tipset
Token
Token Economy
Token Generation Event (TGE)
Token Issuance
Token Lockup
Token Migration
Token Sale
Token Standard
Token Swap
Tokenize
Tokenized Securities
Tokenized Stocks
Tokenomics
TokenSets (Set Protocol)
Toll Bridge
Tor
Total Exchange Volume
Total Supply
Total Value Locked (TVL)
Trade Volume
Trading Bot
Trading Tournament
Trading Volume
TradingView
Transaction (TX)
Transaction Fee
Transaction Triggers
Transactions Per Second
TRC-10 (TRON)
TRC-20 Token
Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
Treasury Bond (T-Bond)
Trojan
Truffle
Trust
Trustless
Tumbler
Turing-Complete
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Type Checking
TypeScript Programming Language
Typosquatting
Validator
Vanity Address
Vaporware
Venture Capital
Verification Code
Vesting Period
Virgin Bitcoin
Virtual Automated Market Makers (vAMMs)
Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Virtual Reality (VR)
Virus
Vitalik Buterin
Volatility
Volume
Wallet
Wallstreetbets (WSB)
WannaCry Ransomware
Wash Trade
Watchdog Organization
Watchlist
Weak Hands
Web 1.0
Web 2.0
Web 3.0
Web3 Foundation
WebSocket
Wei
Whale
What Is the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN)?
When Lambo
When Moon
White Hat Computer Hacker
White Label
Whitelist
Whitepaper
Winding Down
Winding Up
Recommended Posts
- How to Build a Bug Out Bag for Kids: Tips and Tricks
- 10 Survival Skills Every Kid Should Know
- Food prices are about to skyrocket even more; Prepare for a 'famine,' followed by housing crash, then equities wipeout - Michael Gayed
- South Threatened by Severe Weather After Texas Tornado Disaster: How to Prepare.
- The Ultimate Guide to Radiation Water Filters: How They Work



